What is a tsunami
Tsunami (read tsuːˈnɑːmi/) is a long, high sea wave that is generated when the sea floor unexpectedly deforms and disfigures vertically as an effect of disturbance that occurs beneath the sea floor.
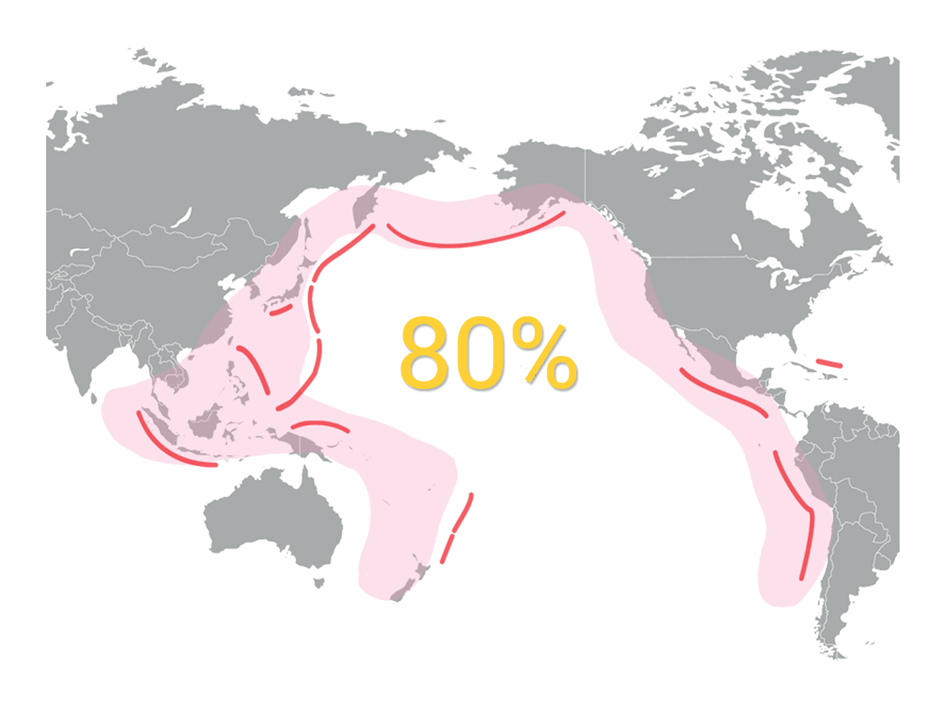
Indonesia is known as the scene of the biggest tsunami in the world, caused by Mount Krakatoa eruption on August 27, 1883. The death toll from the calamity in the Sunda Strait is around 36,000 people. Around 165 towns and villages spread on the coast where hit by tsunami waves as high as 40 meters. In addition to devastating tsunamis caused by volcanic eruptions, Indonesia coastline can be affected by tsunamis that are caused by tectonic earthquakes in the sea floor. At the ocean floor around the country three tectonic plates meet: the Eurasian, Indo-Australian, and Pacific. Disturbance created by those plates shifting often cause earthquakes and volcanic eruptions that have earned the area the name of the ring of fire. The geography itself is dominated by volcanoes that are formed due to subduction zones between the Eurasian plate and the Indo-Australian plate.

Tsunamis in Indonesia
-
There have been 174 tsunamis recorded in Indonesia since 16th century.
-
There have been 32 tsunamis recorded in The Moluccas sea area since 16th century.
-
28 of the Moluccan tsunamis have been caused by earthquakes.
-
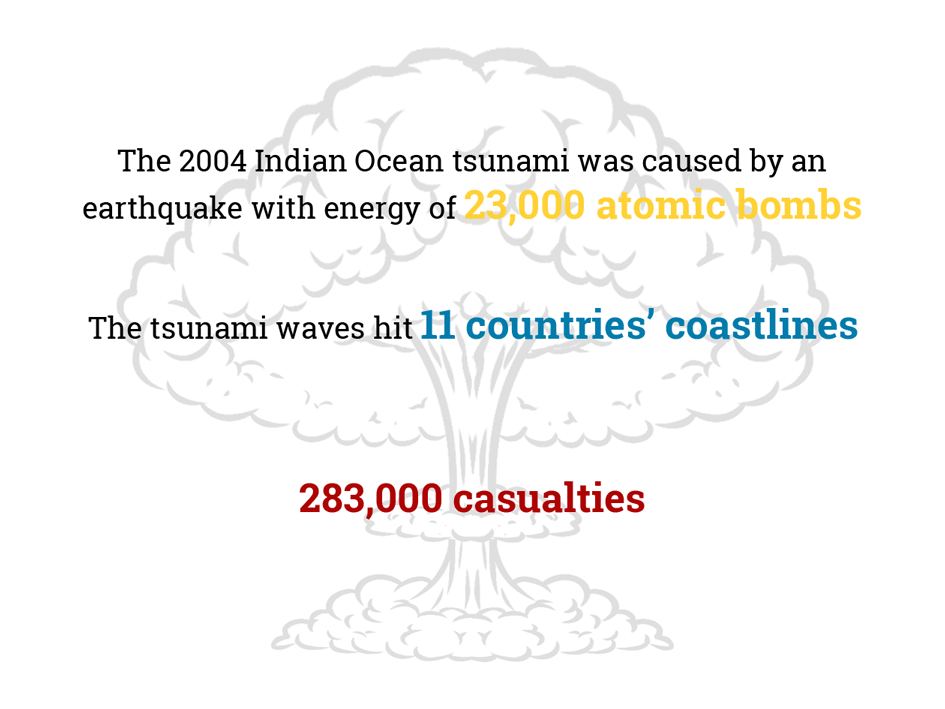
A tsunami caused by Aceh earthquake in 2004 has claimed 200,000 lives.
-
Around 28% (150 of 530) of Indonesian cities are located in tsunami prone areas
- There have been 174 tsunamis recorded in Indonesia since 16th century.
- There have been 32 tsunamis recorded in The Moluccas sea area since 16th century.
- 28 of the Moluccan tsunamis have been caused by earthquakes.
- A tsunami caused by Aceh earthquake in 2004 has claimed 200,000 lives.
- Around 28% (150 of 530) of Indonesian cities are located in tsunami prone areas
-
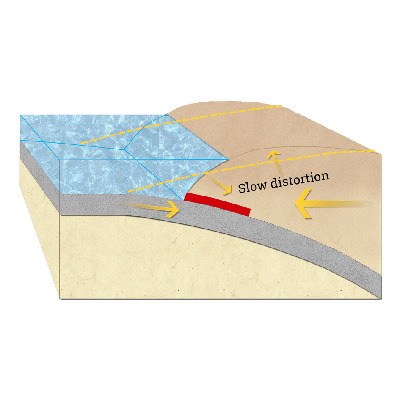
Vertical Slice Through a Subduction Zone
Step 1
One of the many tectonic plates that make up Earth’s outer shell descends, or “subducts,” under an adjacent plate. This kind of boundary between plates is called a “subduction zone.” When the plates move suddenly in an area where they are usually stuck, an earthquake happens.
-
Between Earthquakes
Step 2
Stuck to the subducting plate, the overriding plate gets squeezed. Its leading edge is dragged down, while an area behind bulges upward. This movement goes on for decades or centuries, slowly building up stress.
-
During an Earthquake
Step 3
An earthquake along a subduction zone happens when the leading edge of the overriding plate breaks free and springs seaward, raising the sea floor and the water above it. This uplift starts a tsunami. Meanwhile, the bulge behind the leading edge collapses, thinning the plate and lowering coastal areas.
-
Minutes later
Step 4
Part of the tsunami races toward nearby land, growing taller as it comes in to shore. Another part heads across the ocean toward distant shores.
-
Tsunami
reaches the coast
in ~30min
Interesting facts about tsunamis

Tsunami in Indonesia
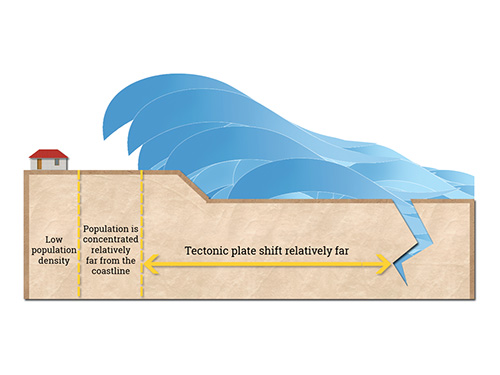
- Tectonic plate shifts occur relatively close to the coastline.
- Population is concentrated closer to the shore.
- Nearly flat coast topography increases the risk of devastating events even further.
- The average tsunami wave travel times is only 30 minutes
This means advanced early warning systems and disaster mitigation management are required to avoid casualties.